Welcome, fellow coders, to another illuminating blog post on Flexteck! Today, we embark on a journey into the fundamental elements of C programming - Identifiers and Keywords. Understanding these building blocks is crucial for anyone diving into the world of C. Let's unravel the mysteries together!
In this blog post, we will learn about two important concepts in C programming: identifiers and keywords. We will see what they are, how they are used, and what rules we need to follow when naming them.
Keywords in C:
What are Keywords?
In C, keywords are reserved words that have predefined meanings in the language. These words serve specific purposes and cannot be used as identifiers (names given to variables, functions, etc.). Examples of C keywords include int, float, if, for, and while.
How Many Keywords Are in C?
The number of keywords in C may vary depending on the compiler or the standard version of C. However, the ANSI C standard defines 32 keywords as follows:
auto double int struct
break else long switch
case enum register typedef
char extern return union
const float short unsigned
continue for signed void
default goto sizeof volatile
do if static while
Use of Keywords in C:
Keywords play a crucial role in defining the syntax and structure of C programs. They indicate the type of data, control flow, and other essential functionalities. Proper use of keywords ensures that your code is correctly interpreted by the compiler. For example:
int, char, float, double, etc. are used to define data types for variables and constants.
if, else, switch, case, etc. are used to implement conditional statements or branching.
for, while, do-while, etc. are used to implement looping or iteration.
break, continue, goto, etc. are used to alter the flow of control in a program.
return, void, etc. are used to specify the return type or value of a function.
const, volatile, etc. are used to modify the behavior or properties of a variable or a function.
typedef, struct, union, enum, etc. are used to create user-defined data types or structures.
Identifiers in C:
What are Identifiers?
Identifiers are user-defined names that are given to variables, constants, functions, arrays, pointers, structures, etc. They are used to identify and refer to these elements in a program. For example:
int x; // x is an identifier for an integer variable
char name[20]; // name is an identifier for a character array
float area(float r); // area is an identifier for a function that takes a float parameter and returns a float value.
Rules for Identifiers:
here are some rules that we need to follow when naming identifiers in C. They are:
Start with a Letter or Underscore:
Identifiers must begin with a letter (uppercase or lowercase) or an underscore
_.
Subsequent Characters:
Following the first character, an identifier can contain letters, digits, or underscores.
Case-Sensitivity:
C is case-sensitive; thus,
myVarandmyvarare different identifiers.
Reserved Keywords:
Avoid using C keywords as identifiers to prevent conflicts.
special character:
An identifier cannot contain any special symbols or characters other than underscore (_), such as `@, #, $, %, &, *,` etc.
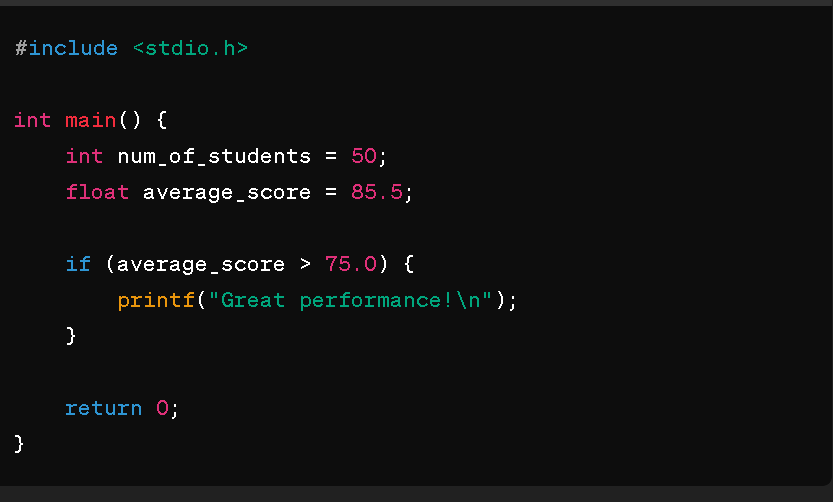
Now, let's weave this knowledge into an example:
Here, num_of_students and average_score are identifiers, while int, float, if, and printf are keywords.
Conclusion:
Mastering identifiers and keywords is akin to unlocking the doors to the language of C. Keywords provide the syntax, and identifiers personalize your code. Embrace these fundamentals, and your C programming journey will flourish!
Happy coding!
Stay tuned for more tutorials and coding adventures!
Subscribe to Flexteck on Substack | Flexteck's YouTube Channel
#CProgramming #IdentifiersInC #KeywordsInC #ProgrammingBasics #FlexteckTutorials #CodingFundamentals #LearnToCode #Programming101